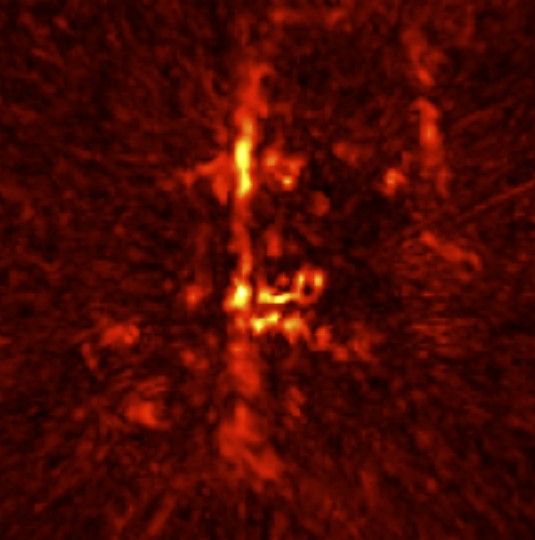
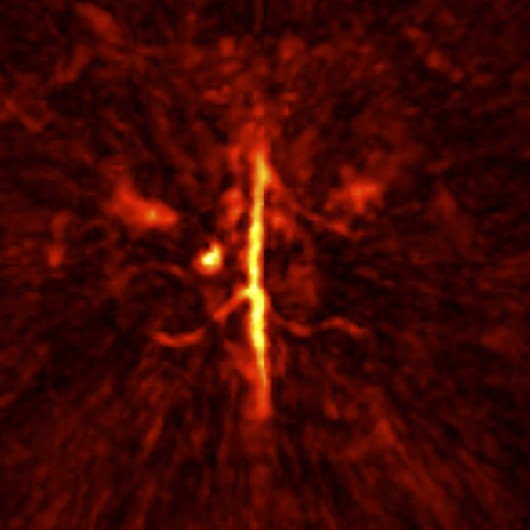
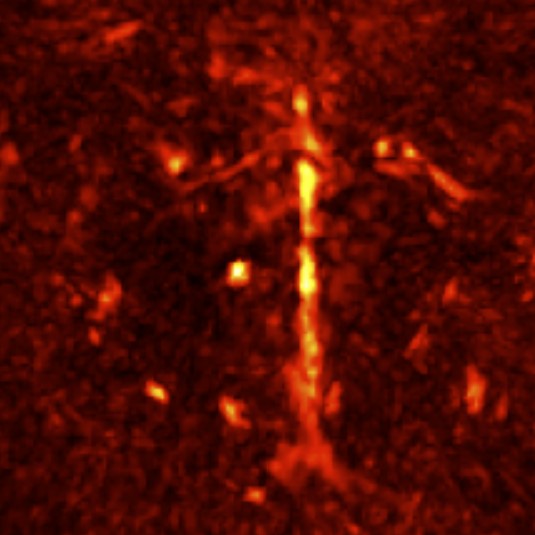
3D MRI-optoacoustic image registration
Deep learning based, fully automatic
Multispectral optoacoustic tomography (MSOT) is an imaging technology that generates high-resolution optical images in biological tissues. It allows measurements of higher spatial resolution than conventional diffuse optical methods, while being non-invasive and non-ionizing. However, it suffers from comparably poor soft-tissue or anatomical contrast. To study the images from anatomical perspective in research, registration is usually required with MRI.
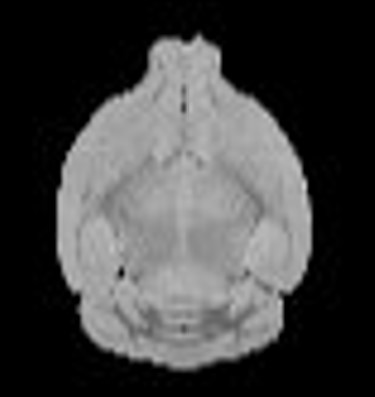
The co-registration between these two imaging modalities is currently done mannually via software such as PMOD, or semi-automatically via some algorithm. Either way, there is a lot of mannual work required even for the latter. Since both images are 3D and very different in appearance, the process can be time-consuming and painful unfortunately. Thus, a fully automatic pipeline would be so great!
The solution involves with the segmentation of brain in each imaging modality through U-net, and then the registration between two brain masks (DL-based or optimization-based can both do the job!). The error function can be chosen as RMSE, BCE, Dice, or you can explore your own to optimize the prediction.
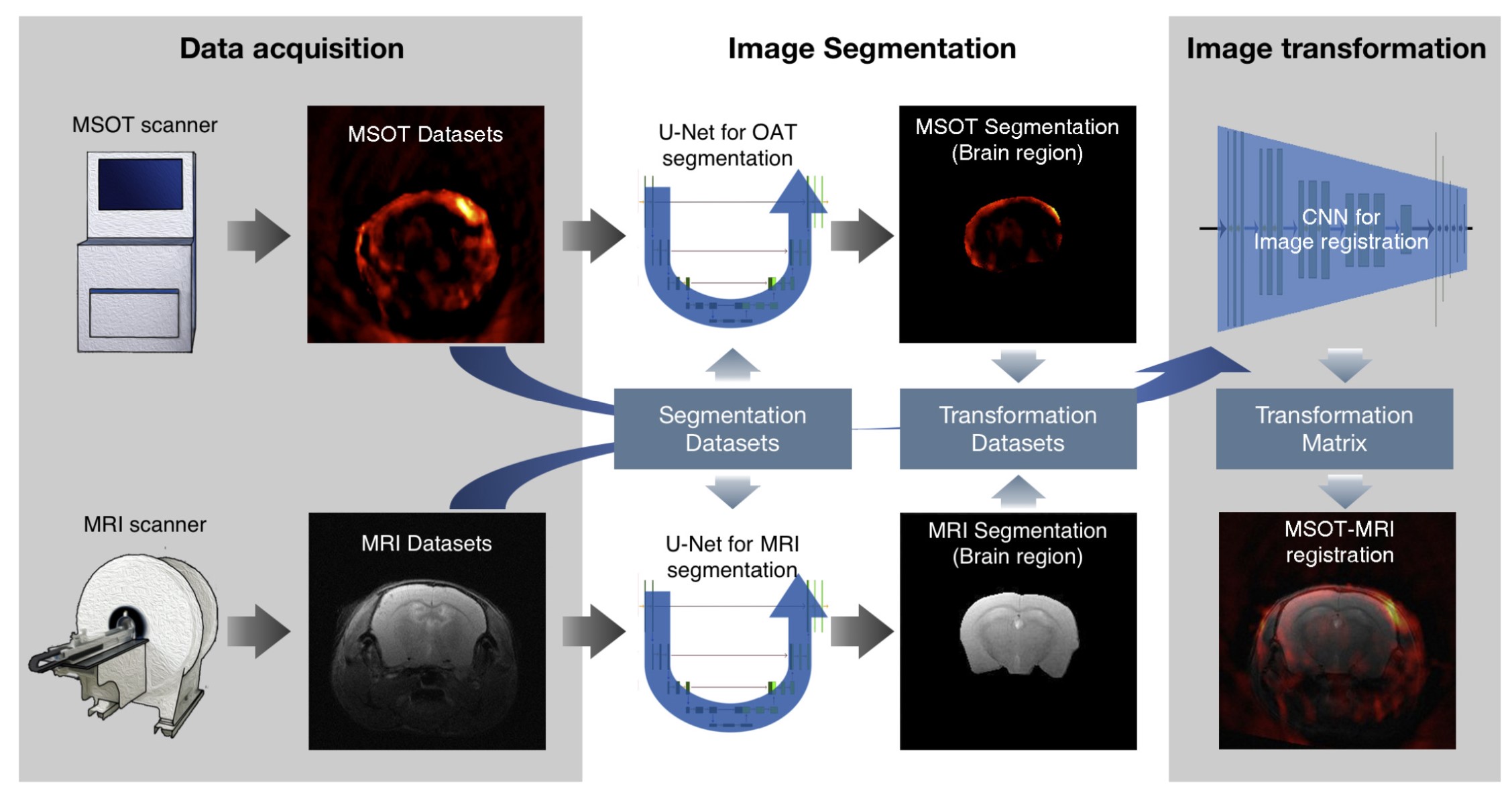
Of course, directly expanding 2D U-net to 3D is not that simple becasue 3D volumetric data contains a lot more information than 2D. Since annonated 3D medical images are usually very limited in number, this will easily lead to overparameterization. So besides regular data augmentation like rotation, translation, and scaling, we use Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) such as DCGAN and cycleGAN to generate realistic images. This helps us boost the number of training data and fight against overparameterization.